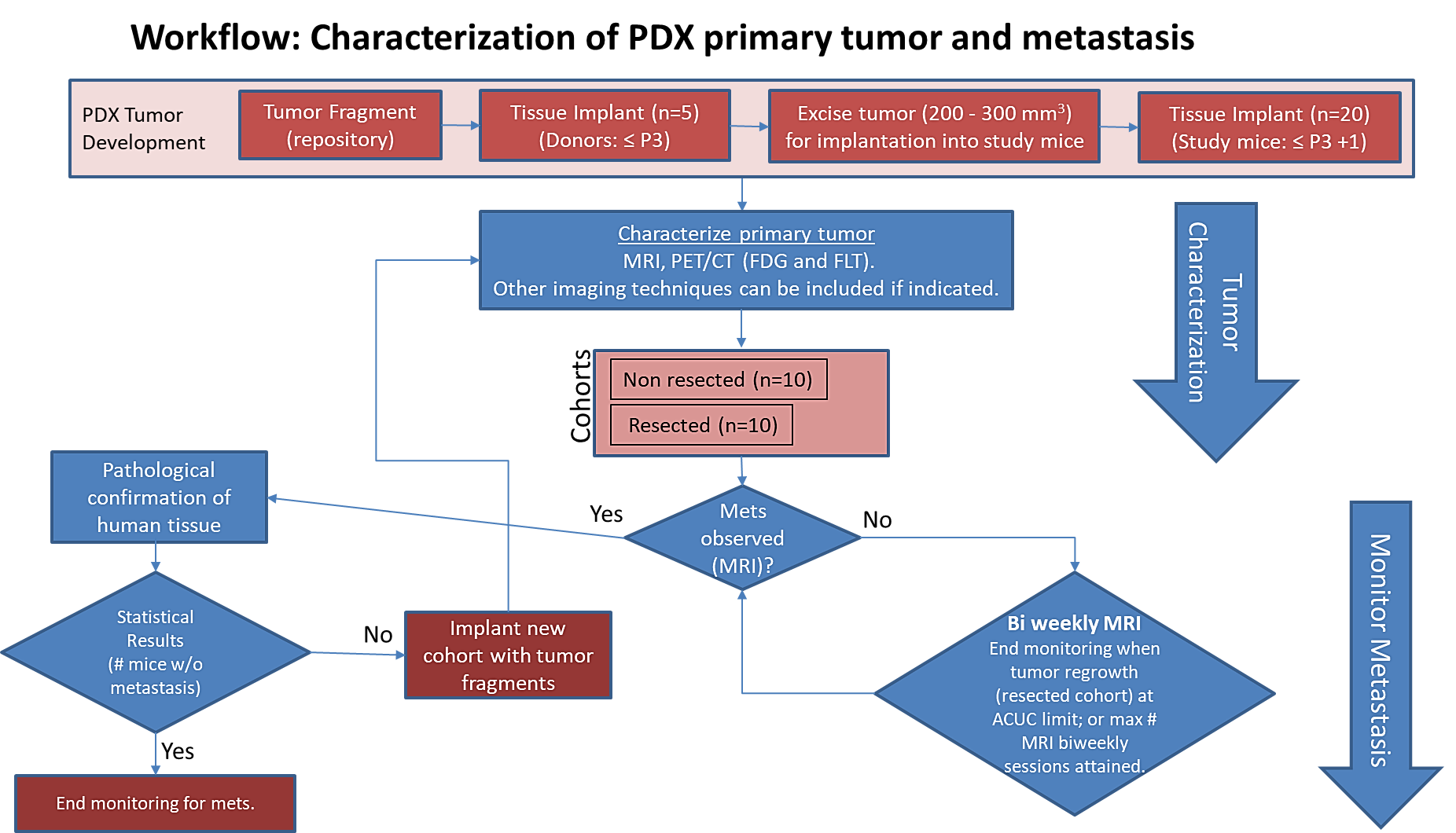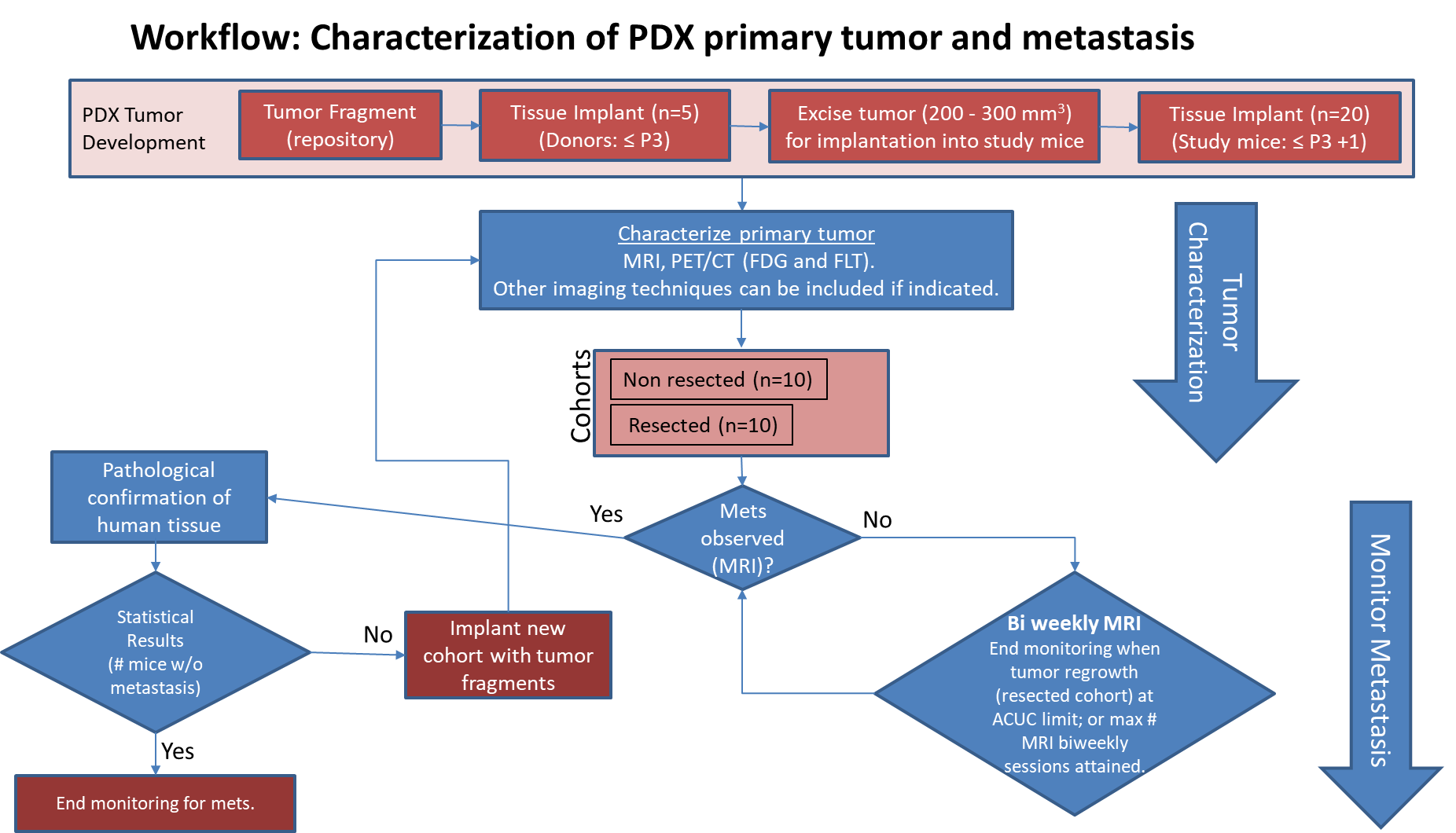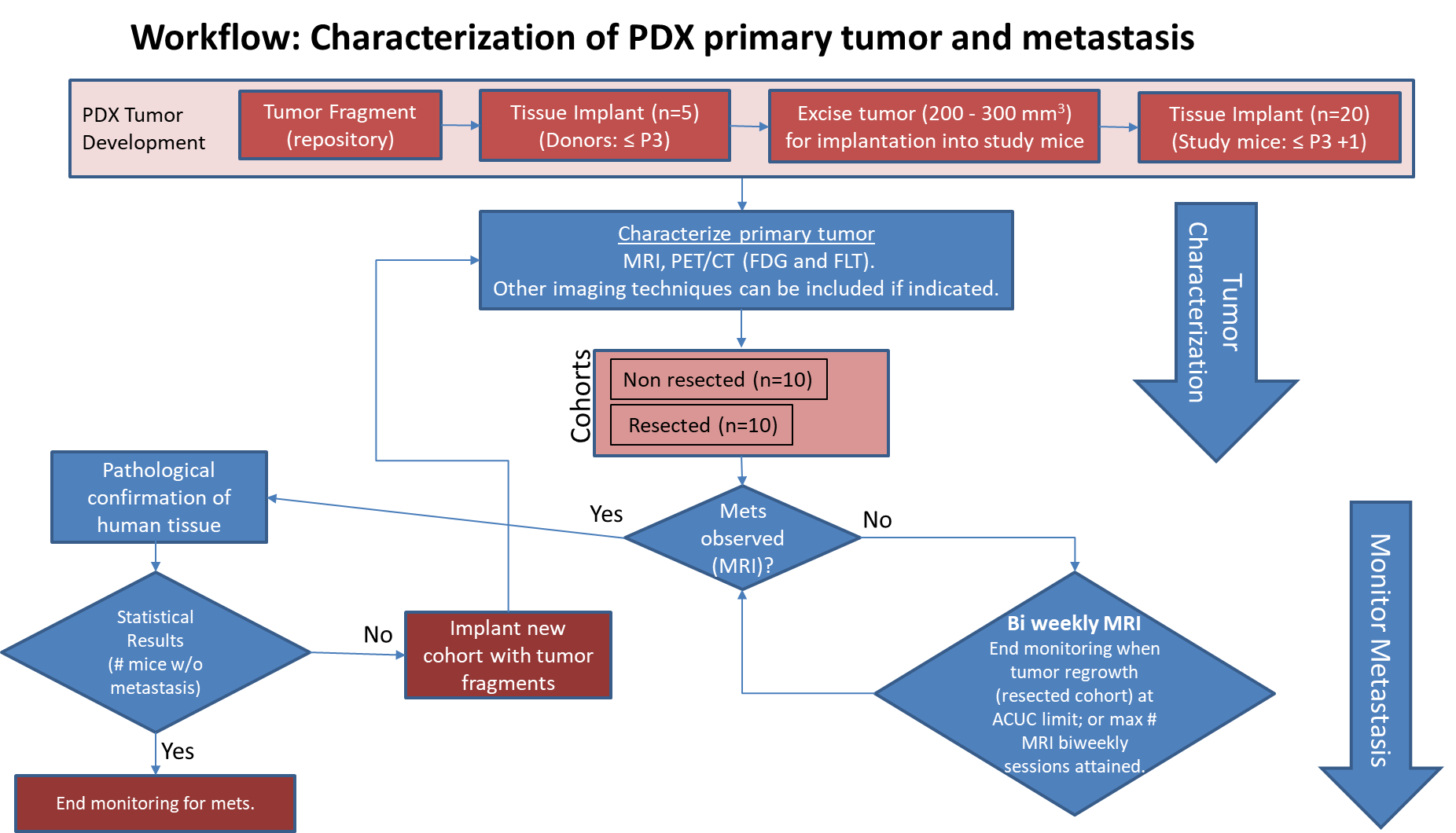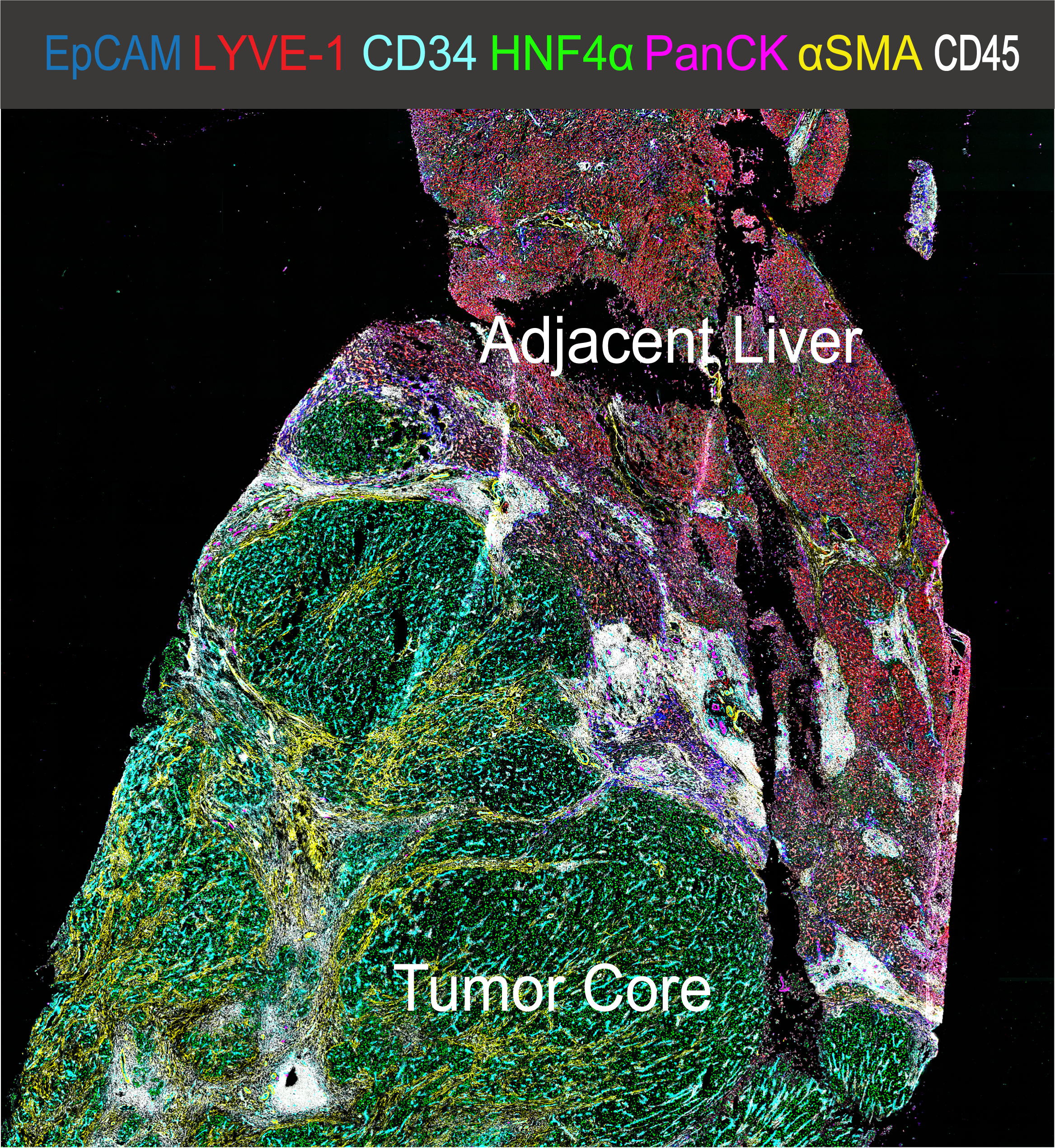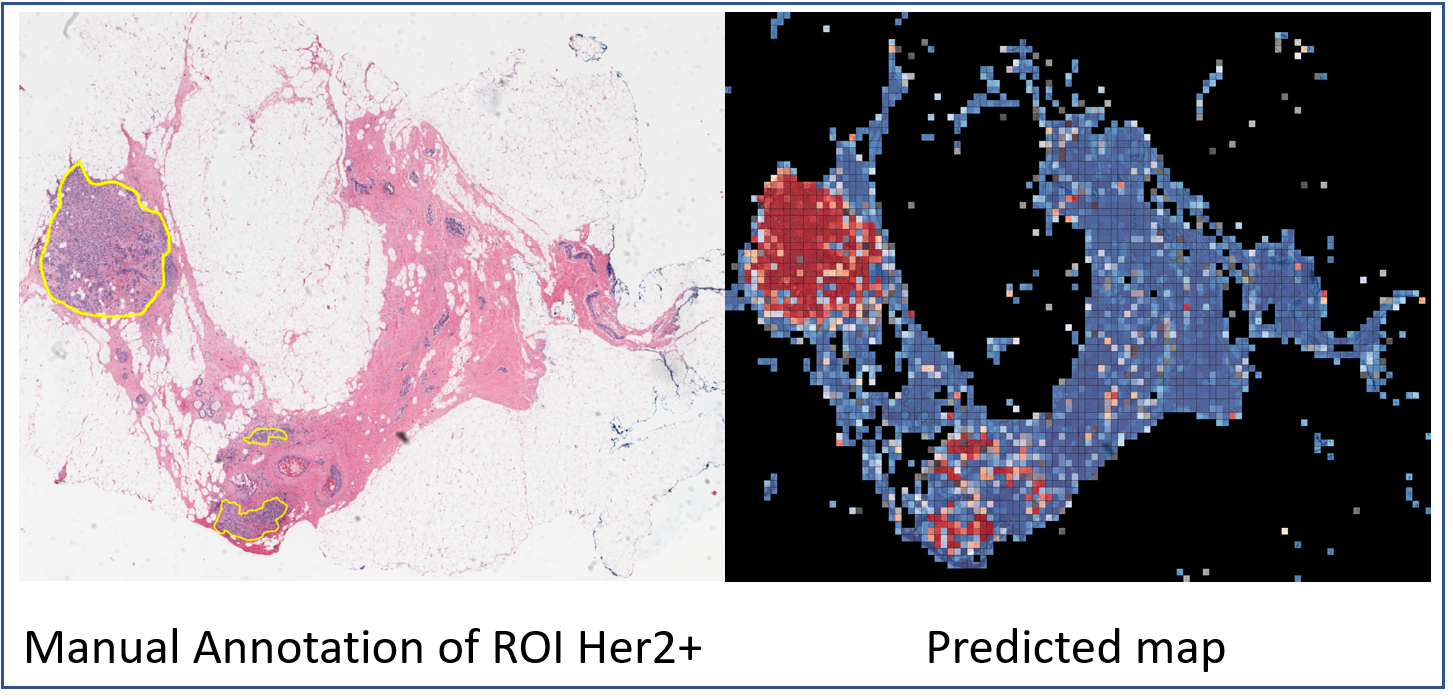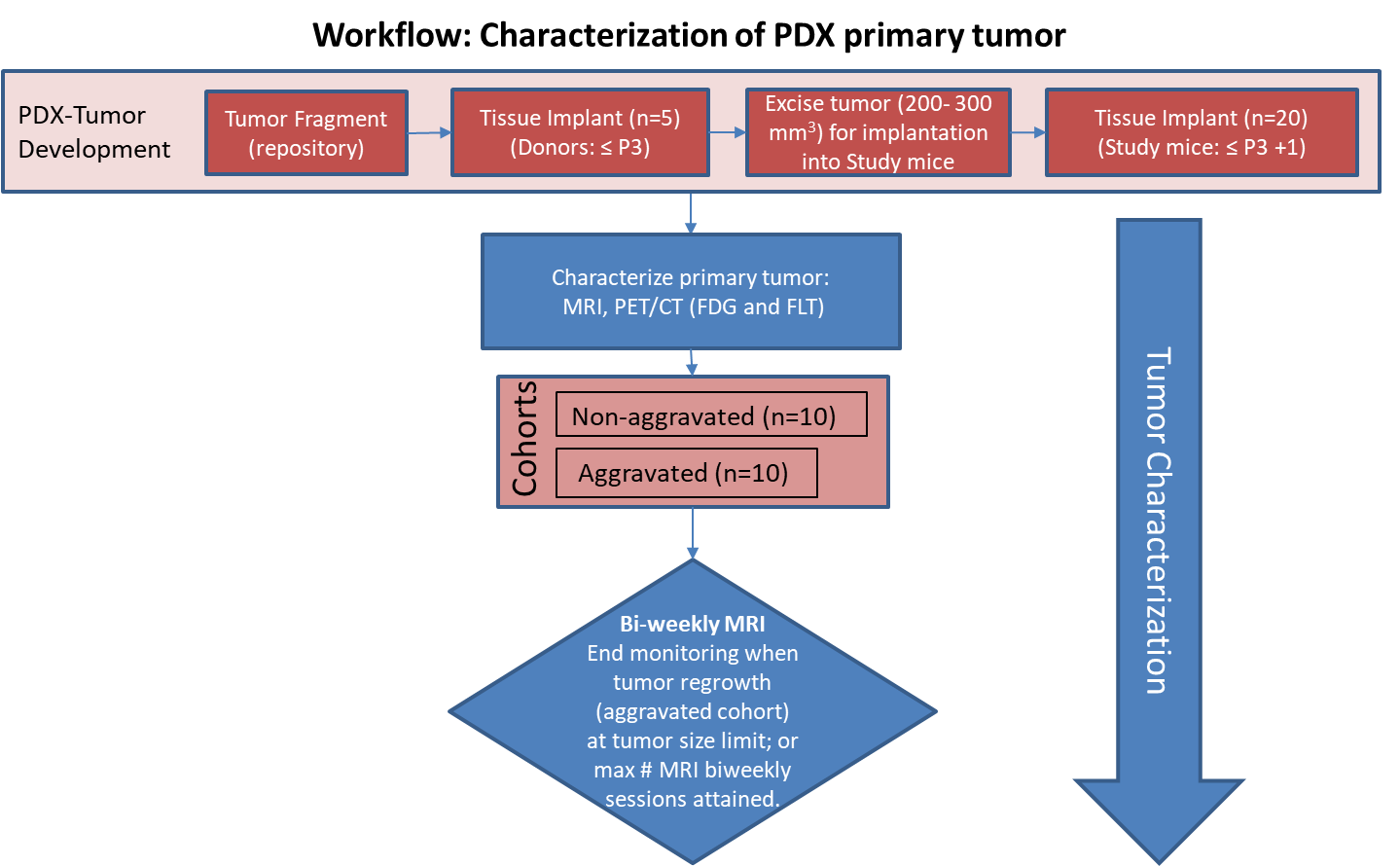
Characterization of tissue using in vivo non-invasive imaging is the foundation of Radiology and is clinically used for detection and measurement of disease burden in oncology. With the migration of imaging to digital media the possibility for advanced mathematically based imaging biomarkers was realized. As part of this endeavor, researchers have developed various algorithms using neural networks, and classification...