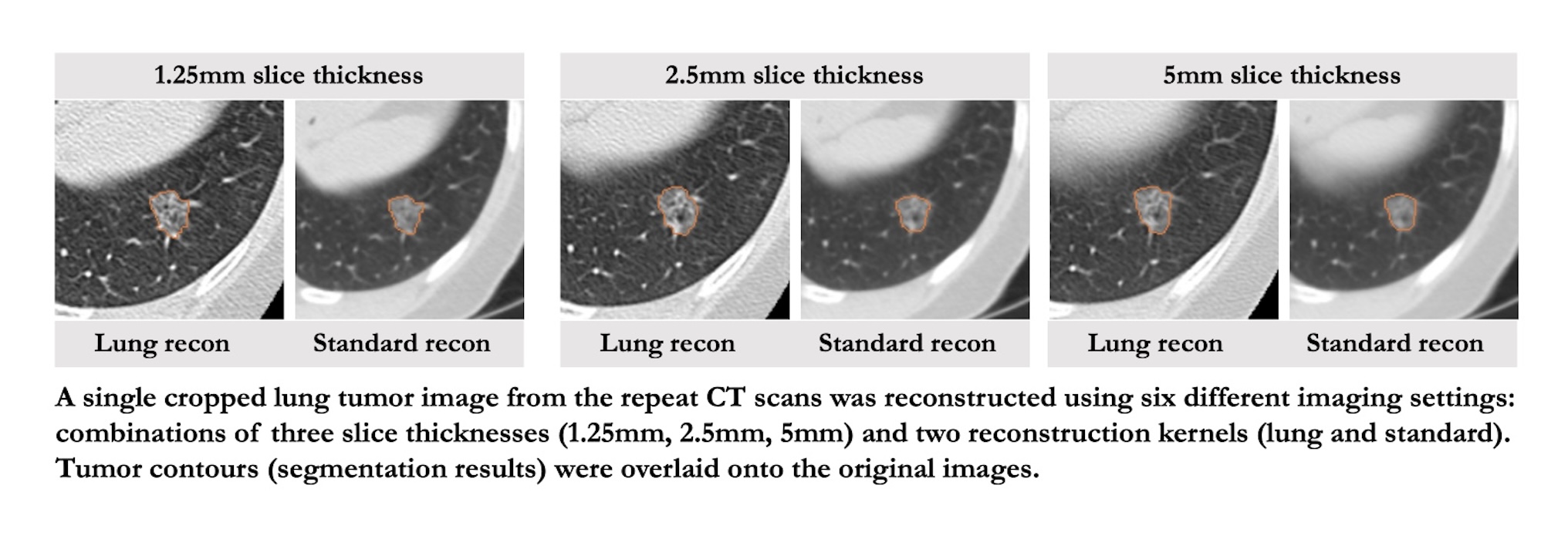
RIDER Lung CT | Coffee-break lung CT collection with scan images reconstructed at multiple imaging parameters
DOI: 10.7937/k9/tcia.2015.u1x8a5nr | Data Citation Required | Image Collection
| Location | Species | Subjects | Data Types | Cancer Types | Size | Status | Updated | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chest | Human | 32 | CT, SEG | Lung Cancer | Image Analyses | Public, Complete | 2024/06/25 |
Summary
Quantitative imaging biomarkers (QIB) are increasingly used in clinical research to advance precision medicine approaches in oncology. Unlike biopsy-based biomarkers, QIBs are non-invasive and can estimate the spatial and temporal heterogeneity of total tumor burden. Computed tomography (CT) is a modality of choice for cancer diagnosis, prognosis, and response assessment due to its reliability and global accessibility. In recent years, despite overwhelmingly increased awareness of the reproducibility and robustness in quantitative imaging studies, lack of precious clinical image data limits our investigation and algorithm development. Here, we contribute to the cancer imaging community with our investigator-initiated, same-day repeat CT scan images of 32 non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients, along with radiologist’s annotated lesion contours as the reference standard. Each scan was reconstructed into 6 image settings using various combinations of three slice thicknesses (1.25 mm, 2.5 mm, 5 mm) and two reconstruction kernels (lung, standard; GE CT equipment), which spans a wide range of CT imaging reconstruction parameters commonly used in lung cancer clinical practice and clinical trials. One of the 6-settings, i.e., the setting of 1.25mm slice thickness and lung reconstruction (1.25L), was published as part of the Reference Image Database to Evaluate Therapy Response (RIDER) project in 2012. We believe that this entire dataset, comprising CT lung cancer images reconstructed on the same day at six different image settings, holds considerable value for advancing the development of robust Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) methods. Additionally, it provides a valuable resource for comparing QIBs derived from a wide range of CT imaging parameter settings, for investigating data harmonization approaches, and for identifying specific CT imaging parameters most suitable for studying radiomics in lung cancer. Design Type(s) database creation objective • data integration objective • image analysis objective Measurement Type(s) non-small cell lung carcinoma Technology Type(s) computed tomography scanner • image segmentation Factor Type(s) repeat scans • image reconstruction settings Sample Characteristic(s) Homo sapiens • lung
Data Access
Version 3: Updated 2024/06/25
Added new CT and SEG series for all patients.
| Title | Data Type | Format | Access Points | Subjects | License | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Images | CT, SEG | DICOM | Download requires NBIA Data Retriever |
32 | 100 | 936 | 81,548 | CC BY 4.0 |
| Lesion Notes | XLS | CC BY 3.0 |
Additional Resources for this Dataset
The NCI Cancer Research Data Commons (CRDC) provides access to additional data and a cloud-based data science infrastructure that connects data sets with analytics tools to allow users to share, integrate, analyze, and visualize cancer research data.
- Imaging Data Commons (IDC) (Imaging Data)
Citations & Data Usage Policy
Data Citation Required: Users must abide by the TCIA Data Usage Policy and Restrictions. Attribution must include the following citation, including the Digital Object Identifier:
Data Citation |
|
|
Zhao, B., Schwartz, L. H., Kris, M. G., & Riely, G. J. (2015). Coffee-break lung CT collection with scan images reconstructed at multiple imaging parameters (Version 3) [Dataset]. The Cancer Imaging Archive. https://doi.org/10.7937/k9/tcia.2015.u1x8a5nr |
Related Publications
Publication Citation |
|
|
Zhao, B., James, L. P., Moskowitz, C. S., Guo, P., Ginsberg, M. S., Lefkowitz, R. A., Qin, Y., Riely, G. J., Kris, M. G., & Schwartz, L. H. (2009). Evaluating Variability in Tumor Measurements from Same-day Repeat CT Scans of Patients with Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. In Radiology (Vol. 252, Issue 1, pp. 263–272). Radiological Society of North America (RSNA). https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2522081593 |
Research Community Publications
TCIA maintains a list of publications which leverage our data.
- Radiomics of Lung Nodules: A Multi-Institutional Study of Robustness and Agreement of Quantitative Imaging Features. DOI:10.18383/j.tom.2016.00235
- Textural Analysis of Tumour Imaging: A Radiomics Approach. https://lib.ugent.be/catalog/rug01:002367219
If you have a manuscript you’d like to add please contact TCIA’s Helpdesk.
Previous Versions
Version 1: Updated 2012/10/18
Initial upload of data set.
| Title | Data Type | Format | Access Points | License |
|---|
Version 2: Updated 2014/11/14
It was brought to our attention that the RIDER-8509201188 patient contained 2 identical image series rather than the correct secondary/repeat series. The duplicate series has been removed (UID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.9328.50.1.64033480205396366773922006817138551096), but we are unable to obtain the correct series at this point.
| Title | Data Type | Format | Access Points | License | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Images | SEG, CT | DICOM | Download requires NBIA Data Retriever |
32 | 46 | 153 | 15,509 | CC BY 3.0 |
| DICOM Metadata Digest | CSV | CC BY 3.0 | ||||||
| Lesion Notes | XLS | CC BY 3.0 |