CTpred-Sunitinib-panNET | Prediction of Sunitinib Efficacy using Computed Tomography in Patients with Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors
DOI: 10.7937/SPGK-0P94 | Data Citation Required | Image Collection
| Location | Species | Subjects | Data Types | Cancer Types | Size | Status | Updated |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pancreas | Human | 38 | CT | Pancreas Cancer | Public, Complete | 2022/09/12 |
Summary
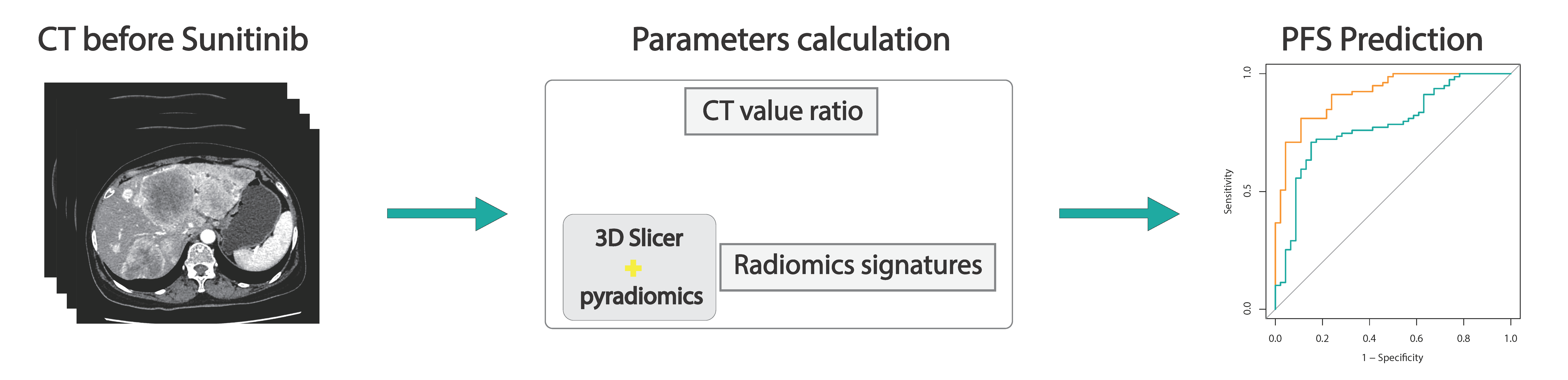
Clinically effective methods to predict the efficacy of sunitinib, for patients with metastatic or locally advanced pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (panNET) are scarce, making precision treatment difficult. This study aimed to develop and validate a computed tomography (CT)-based method to predict the efficacy of sunitinib in patients with panNET.
Pretreatment CT images of 171 lesions from 38 patients with panNET were included. Clinical information including sex, age at diagnosis, progression-free survival of sunitnib treatment, ki-67 index, tumor grade and previous treatment before sunitinib were also collected. CT value ratio (CT value of tumor/CT value of abdominal aorta from the same patient) and radiomics features were extracted for model development. Receiver operating curve (ROC) with area under the curve (AUC) and decision curve analysis (DCA) were used to evaluate the proposed model. Tumor shrinkage of >10% at first follow-up after sunitinib treatment was significantly associated with longer progression-free survival (PFS; P<0.001) and was used as the major treatment outcome. The CT value ratio could predict tumor shrinkage with AUC of 0.759 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.685–0.833). We then developed a radiomics signature, which showed significantly higher AUC in training (0.915; 95% CI, 0.866–0.964) and validation (0.770; 95% CI, 0.584–0.956) sets than CT value ratio. DCA also confirmed the clinical utility of the model. Subgroup analysis showed that this radiomics signature had a high accuracy in predicting tumor shrinkage both for primary and metastatic tumors, and for treatment-naive and pretreated tumors. Survival analysis showed that radiomics signature correlated with PFS (P=0.020). The proposed radiomics-based model accurately predicted tumor shrinkage and PFS in patients with panNET receiving sunitinib and may help select patients suitable for sunitinib treatment. Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors is a rare group of tumor. The dataset can be used to validate the findings of our study. More importantly, researchers can use this dataset to study the imaging characteristics of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors.
Data Access
Version 1: Updated 2022/09/12
| Title | Data Type | Format | Access Points | Subjects | License | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Images | CT | DICOM | Download requires NBIA Data Retriever |
38 | 76 | 76 | 22,474 | CC BY 4.0 |
| Clinical data | CSV | CC BY 4.0 |
Additional Resources for this Dataset
The NCI Cancer Research Data Commons (CRDC) provides access to additional data and a cloud-based data science infrastructure that connects data sets with analytics tools to allow users to share, integrate, analyze, and visualize cancer research data.
Citations & Data Usage Policy
Data Citation Required: Users must abide by the TCIA Data Usage Policy and Restrictions. Attribution must include the following citation, including the Digital Object Identifier:
Data Citation |
|
|
Chen, L., Wang, W., Jin, K., Yuan, B., Tan, H., Sun, J., Guo, Y., Luo, Y., Feng, S.-ting, Yu, X., Chen, M.-hu, & Chen, J. (2022). Prediction of Sunitinib Efficacy using Computed Tomography in Patients with Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors (CTpred-Sunitinib-panNET) (Version 1) [Data set]. The Cancer Imaging Archive. https://doi.org/10.7937/SPGK-0P94 |
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82141104), Guangzhou Science and Technology Plan (No. 201804010078), and Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (No. 2019A1515011373). This study was also partially supported by Pfizer Oncology Medical Affairs. However, Pfizer did not take part in data collection, analysis and interpretation.
Related Publications
Publication Citation |
|
|
Chen, L., Wang, W., Jin, K., Yuan, B., Tan, H., Sun, J., Guo, Y., Luo, Y., Feng, S., Yu, X., Chen, M., & Chen, J. (2022). Special issue “The advance of solid tumor research in China”: Prediction of Sunitinib Efficacy Using Computed Tomography in Patients with Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors. In International Journal of Cancer. Wiley. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.34294 |
Research Community Publications
TCIA maintains a list of publications which leverage TCIA data. If you have a manuscript you’d like to add please contact the TCIA Helpdesk.
