CT-Phantom4Radiomics | Task-Based Anthropomorphic CT Phantom for Radiomics Stability and Discriminatory Power Analyses
DOI: 10.7937/a1v1-rc66 | Data Citation Required | Image Collection
| Location | Species | Subjects | Data Types | Cancer Types | Size | Status | Updated | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phantom | Human | 1 | SEG, CT | Phantom | Image Analyses, Software/Source Code | Public, Complete | 2023/08/23 |
Summary
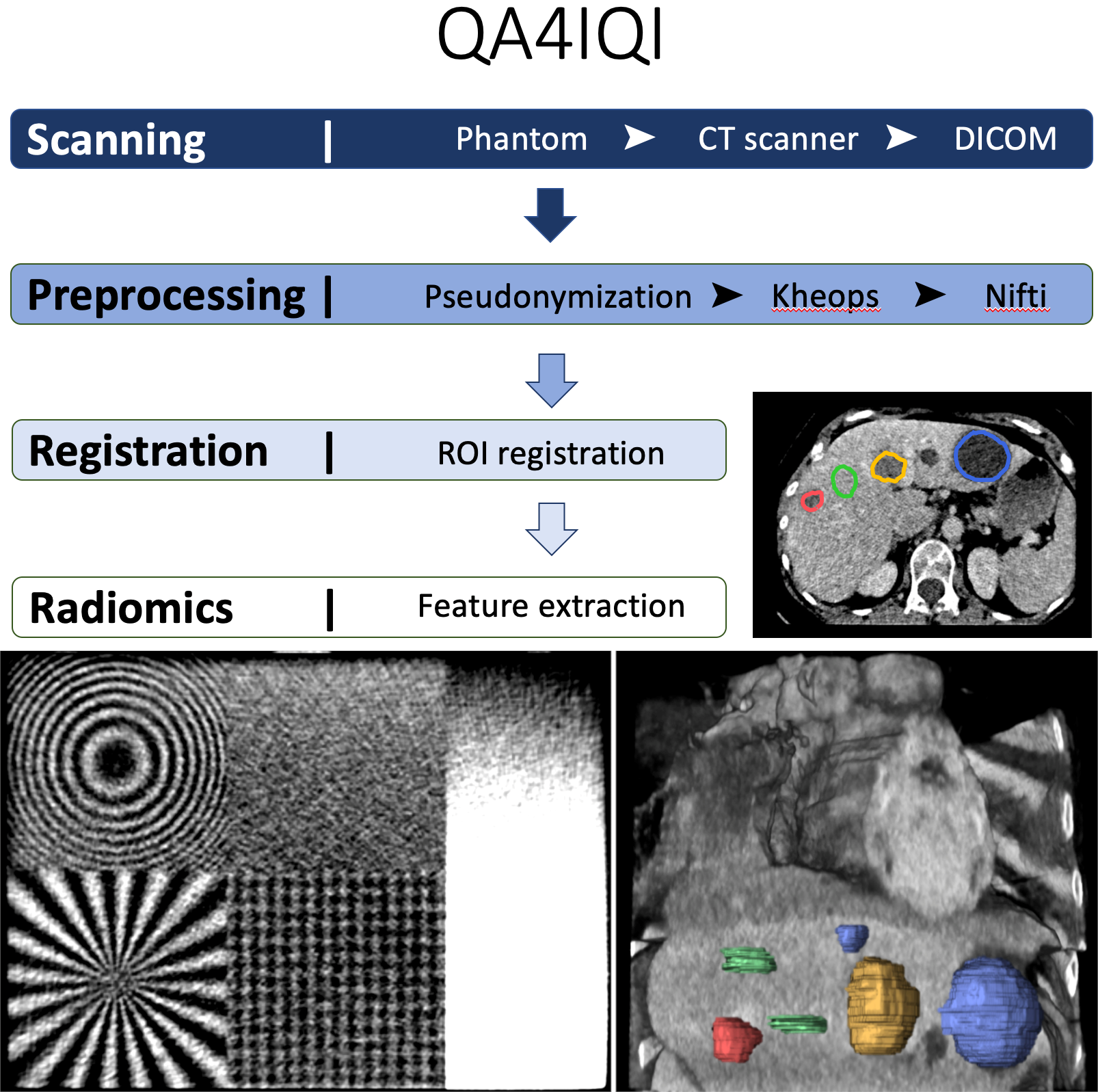
The aims of this dataset are to determine the stability of radiomics features against computed tomography (CT) parameter variations and to study their discriminative power concerning tissue classification using a 3D-printed CT phantom based on real patient data. A radiopaque 3D phantom was developed using real patient data and a potassium iodide solution paper-printing technique. Normal liver tissue and 3 lesion types (benign cyst, hemangioma, and metastasis) were manually annotated in the phantom. 238 CT series with 8 parameter variations of reconstruction algorithms, reconstruction kernels, slice thickness, and slice spacing are available. In a preliminary study, we showed that the 8 CT parameter variation pairwise group comparisons had statistically significant differences on average in 78/86 radiomics features. On the other hand, 84% of the univariate radiomics feature tests had a successful and statistically significant differentiation of the 4 classes of liver tissue. We concluded that the differences in radiomics feature values obtained from different types of liver tissue are generally greater than the intraclass differences resulting from CT parameter variations. The phantom was printed using the Phantom X solution detailed in the study, "Radiopaque Three-dimensional Printing: A Method to Create Realistic CT Phantoms". It relies on inkjet cartridges filled with potassium iodide solutions (600 mg/mL) with prints realized on plain paper (80 g/m2). Stacked paper sheets result in three-dimensional phantoms. Because the printing process is very specific to the Phantom X company and no other printer can be used, we did not make the printer creation file publicly available. This dataset can serve as a reference to assess both the discriminative power and stability of radiomics features with CT variations. In addition, it can be used to develop efficient data harmonization techniques to improve robustness of (deep) radiomics features and models. Additional information and source code related to the project can be found at https://qa4iqi.github.io/.
Data Access
Version 1: Updated 2023/08/23
| Title | Data Type | Format | Access Points | Subjects | License | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Images & Segmentations | SEG, CT | DICOM | Download requires NBIA Data Retriever |
1 | 238 | 476 | 78,452 | CC BY 4.0 |
Additional Resources for this Dataset
The following external resources have been made available by the data submitters. These are not hosted or supported by TCIA, but may be useful to researchers utilizing this collection.
- Additional information about the QA4IQI project, as well as a link to a repository containing source code & instructions for running the radiomics feature extraction pipeline on the dataset can be found at https://qa4iqi.github.io.
The NCI Cancer Research Data Commons (CRDC) provides access to additional data and a cloud-based data science infrastructure that connects data sets with analytics tools to allow users to share, integrate, analyze, and visualize cancer research data.
- Imaging Data Commons (IDC) (Imaging Data)
Citations & Data Usage Policy
Data Citation Required: Users must abide by the TCIA Data Usage Policy and Restrictions. Attribution must include the following citation, including the Digital Object Identifier:
Data Citation |
|
|
Schaer, R., Bach, M., Obmann, M., Flouris, K., Konukoglu, E., Stieltjes, B., Müller, H., Aberle, C., Jimenez del Toro, O. A., & Depeursinge, A. (2023). Task-Based Anthropomorphic CT Phantom for Radiomics Stability and Discriminatory Power Analyses (CT-Phantom4Radiomics) [Data set]. https://doi.org/10.7937/a1v1-rc66 |
Acknowledgements
- This work was partly supported by the Swiss Personalized Health Network (SPHN) with the QA4IQI Quality assessment for interoperable quantitative computed tomography imaging project (DMS2445) and the IMAGINE project (2018DRI10).
- It was also partially supported by the Swiss National Science Foundation (SNSF, grant 205320_179069), as well as the HES-SO 2022 Open Data Project Call.
Related Publications
Publication Citation |
|
|
Jimenez-del-Toro, O., Aberle, C., Bach, M., Schaer, R., Obmann, M. M., Flouris, K., Konukoglu, E., Stieltjes, B., Müller, H., & Depeursinge, A. (2021). The Discriminative Power and Stability of Radiomics Features With Computed Tomography Variations. In Investigative Radiology (Vol. 56, Issue 12, pp. 820–825). Ovid Technologies (Wolters Kluwer Health). https://doi.org/10.1097/rli.0000000000000795 |
Research Community Publications
The following publications are recommended by the data submitters that may be useful to researchers utilizing this collection:
- Bach, M., Aberle, C., Depeursinge, A., Jimenez‐del‐Toro, O., Schaer, R., Flouris, K., Konukoglu, E., Müller, H., Stieltjes, B., & Obmann, M. M. (2023). 3D‐printed iodine‐ink CT phantom for radiomics feature extraction ‐ advantages and challenges. In Medical Physics. Wiley. https://doi.org/10.1002/mp.16373
TCIA maintains a list of publications which leverage TCIA data. If you have a manuscript you’d like to add please contact TCIA’s Helpdesk.
